Take stock of several recent new drugs of FDA in the United States to speed up the examination and approval
Recently, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a regulatory decision on drugs for the treatment of diffuse large B cells (DLBCL), small cells (SCLC), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), cholangiocarcinoma and graft-versus-host disease. (from FDA)
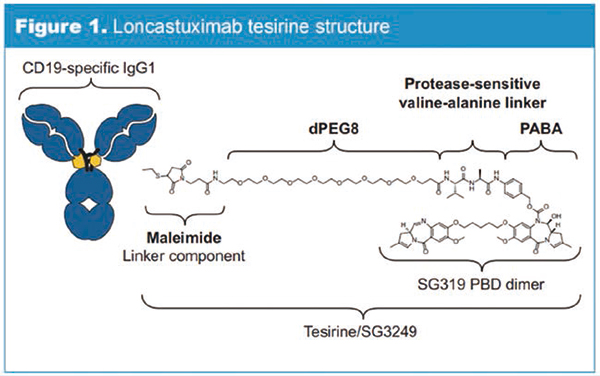
Loncastuximab tesirine in the Treatment of Recurrent/Refractory DLBCL
FDA licensed Loncastuximab based on LOTIS 2 data.
Tesirine treats relapsed/refractory DLBCL, and gives it "priority review" qualification, and sets the target date of PDUFA as May 21st, 2021.
Loncastuximab
Tesirine (formerly known as ADCT-402) is an antibody-drug conjugate, including humanized monoclonal antibody targeting CD19, coupling linker and pyrrole benzodiazepine (PBD) dimer cytotoxin. Once combined with cells expressing CD19, Loncastuximab
Tesirine can be internalized by cells and then the warhead is released. The warhead irreversibly combines with DNA, forming strong cross-linking between strands that can prevent the separation of DNA strands, thus destroying the metabolic process of DNA (such as replication) and eventually leading to cell death.
CD19 is an effective target for clinical treatment of B-cell malignant tumor.
In order to evaluate Loncastuximab
Efficacy and safety of tesirine in the treatment of relapsed/refractory DLBCL patients. Phase II multicenter, open-label single-arm clinical trial LOTIS 2 was included in the relevant patients.
In June, 2020, the mature data was reported at the 25th virtual meeting of the European Hematology Association (abstract S233). By the deadline, Loncastuximab
The total remission rate of tesirine was 48.3%(70/145), and the complete remission rate was 24.1%(35/145). Tolerance can be controlled. The most common events that occur during treatment with an incidence of ≥10% and grade ≥3 are neutropenia (25.5%, febrile neutropenia is 3.4), thrombocytopenia (17.9%), increased γ -glutamyltransferase (16.6%) and anemia (10.3%). Loncastuximab
Tesirine is also being evaluated in LOTIS 3 and LOTIS 5.
Irinotecan liposome injection as second-line monotherapy for SCLC
The FDA approved the fast-track qualification of irinotecan liposome injection for the second-line treatment of SCLC (the first-line platinum-containing regimen failed). At present, the United States and Europe have approved fluorouracil combined with calcium folinate injection to treat advanced and metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma after gemcitabine treatment.
An ongoing phase III randomized trial (RESILIENT) is evaluating the efficacy and safety of irinotecan liposome injection as a monotherapy and second-line treatment for SCLC patients.
Eprenetapopt in the treatment of TP53 mutant AML
The FDA granted Eprenetapopt (also known as APR-246) fast-track qualification to treat patients with TP53 mutant AML. The drug has been qualified for breakthrough therapy, orphan drug and fast track, and is used to treat TP53 mutant myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
Eprenetapopt is a small molecule drug, which can reactivate mutant and inactivated p53 protein by restoring the conformation and function of wild-type p53, thus inducing programmed cell death of human cancer cells. It has preclinical antitumor activity against a variety of solid tumors and hematological cancers (including MDS, AML and so on). In addition, Eprenetapopt has a strong synergistic effect with traditional anticancer drugs (such as chemotherapy), as well as the combination of new mechanism-based anticancer drugs and immune tumor checkpoint inhibitors.
In addition to preclinical experiments, phase I/II clinical trials of Eprenetapopt have proved its good safety and biological and clinical activity in hematological malignancies and solid tumors with TP53 gene mutation.
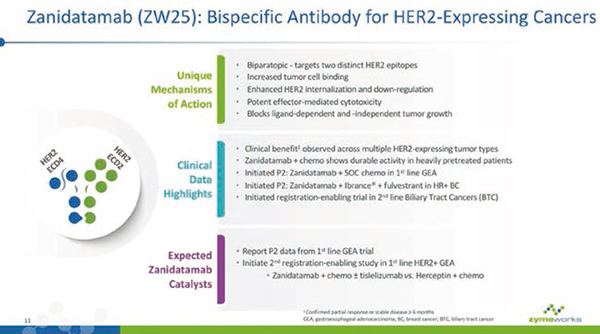
Zanidatamab qualified for breakthrough therapy of cholangiocarcinoma
Based on the ongoing clinical trials in patients with locally advanced/unresectable and/or metastatic HER2-expressing tumors (including cholangiocarcinoma), FDA granted Zanidatamab breakthrough treatment qualification for the treated and HER2-amplified cholangiocarcinoma.
Zanidatamab is a bispecific antibody, which can simultaneously bind two non-overlapping epitopes of HER2 (double complementary binding). This unique design can produce a variety of mechanisms, including double HER2 signal blocking, increased binding, removal of HER2 protein from cell surface and strong effector function leading to anti-tumor activity. Zanidatamab is being studied in a number of phase I, phase II and registry-supported clinical trials around the world for targeted treatment of patients with solid tumors expressing HER2.
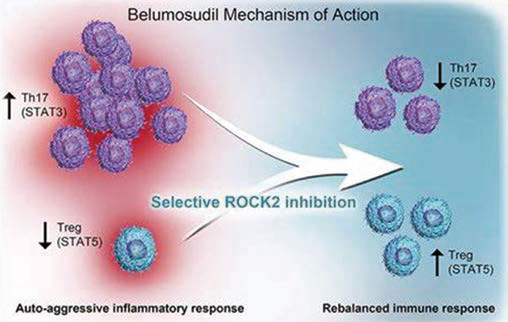
Belumosudil in the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease
Based on ROCKstar(KD025-213) data, FDA gives priority to the review of Belumosudil(KD025) in the treatment of patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease. The review period is 6 months, and the target date of PDUFA is May 30, 2021.
Belumosudil is a ROCK2 inhibitor (ROCK2 is a signal transduction pathway that regulates inflammatory reaction and fibrosis process), and it was once approved by FDA as a "breakthrough therapy" for chronic graft-versus-host disease that failed to be treated by second-line or above systems, and an orphan drug for chronic graft-versus-host disease.
The ongoing open trial ROCKstar(KD025-213) included patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease who failed to receive second-line or above systemic treatment, and randomly assigned them to Belumosudil 200.
Mg qd or 200 mg
Bid, 66 patients were enrolled in each group. The primary end point was the total remission rate. The mid-term analysis after 2 months in the group reached the end point of the total remission rate. In the preliminary analysis of 6 months after the completion of the study, the total remission rate of Belumosudil was 73% and 74% respectively, and it was well tolerated, and the adverse events were consistent with expectations.
Infigratinib in the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma
The FDA accepted the application for new drugs of Infigratinib (oral FGFR1-3 selective inhibitor) to treat patients with cholangiocarcinoma, and it was given priority approval. Infigratinib is an oral, ATP-competitive, FGFR1-3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which is being studied to treat patients with FGFR-driven diseases, including cholangiocarcinoma and urothelial carcinoma.
Treatment equipment for osteoid osteoma of extremity
On November 27th, the FDA approved Sonalleve.
MR-HIFU system for osteoid osteoma of extremities. High-intensity focused ultrasound (MR-HIFU) guided by magnetic resonance is an image-guided technique, which combines high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation and ultrasonic pyrolysis to monitor the temperature change in real time.
Clinical results support Sonalleve.
MR-HIFU system may be beneficial in ablating painful osteoid osteoma. In a study of 9 patients treated by MR-HIFU, no technical difficulties or serious adverse events were found. After 4 weeks of treatment, the pain score was significantly reduced, and 8 cases did not need painkillers.
(Compile Wang Xizhong)